CodeForces 1137F Matches Are Not a Child's Play
题目大意
我们定义一棵树的删除序列为:每一次将树中编号最小的叶子删掉,将该节点编号加入到当前序列的最末端,最后只剩下一个节点时将该节点的编号加入到结尾。
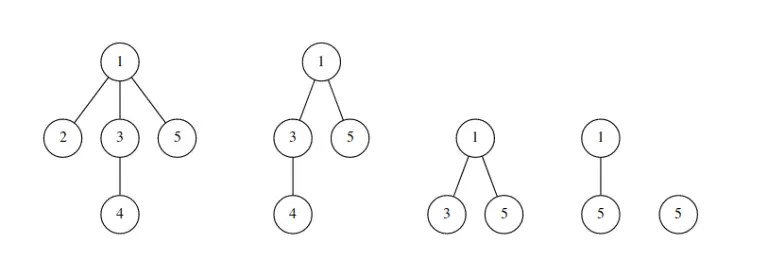
例如对于上图中的树,它的删除序列为:2 4 3 1 5。
现在给出一棵 n 个节点的树,有 m 次操作:
up v:将 v 号节点的编号变为当前所有节点编号的max+1;when v:查询 v 在当前树的删除序列中是第几号元素;compare u v:查询 u 和v在当前树的删除序列中谁更靠前。
输入格式
第一行两个正整数 n,q(1≤n,q≤200000) 表示树的点数和操作数。
接下来 n−1 行每行 2 个正整数 u,v(1≤u,v≤n) 表示树上的一条边。
接下来 q 行每行描述一个操作。
输出格式
每一个询问输出一行。
对于 when v 询问,输出一个正整数表示 v 是当前删除序列的哪一个元素。
对于 compare u v 询问,如果 u 在删除序列中更靠前则输出u,否则输出v。
题解
显然在任意时刻最大的那个节点一定是在最后被删的。
于是我们考虑 up 操作带来的影响。
假设 up 了x,上一次(up前)最大的那个点是y。
我们发现最后删着删着一定只剩下了 x 到y路径上的这几个点。
然后从 y 开始一个一个往 x 那边删。
于是 y∼x 这条链上的点移到了删除序列的末尾。
我们可以把 y∼x 看成一个缩起来的点,我们发现其它点的相对位置不变。
接下来的思路感觉跟 这题 很像。
我们考虑用 LCT 维护这棵树,LCT中的每棵 splay 表示一段连续的删除区间。
开始时根当然是最大的。
样例大概是这样一幅图:

删除序列应该是2 4 3 1 5。
根当然就是最大的那个点。
由于一个 splay 是连续删的。所以我们给每个 splay 一个标号(具体到实现就是给 splay 上每个点染色,可以参考下面的代码),把它放在树状数组上,即在该 splay 的color上加上该 splay 的size。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| inline void dfs(int now)
{
col[now] = now, siz[now] = 1;
for(int i = first[now]; i; i = e[i].nxt)
{
register int to = e[i].to;
if(to != fa[now])
{
fa[to] = now; dfs(to);
if(col[to] > col[now])
{
col[now] = col[to];
s[now][1] = to;
siz[now] = siz[to] + 1;
}
}
}
tr.add(col[now], 1);
}
|
我们考虑查询,就是该点所在 splay 之前的所有点数加上该 splay 上所有该结点后面的点数。
大概就是 树状数组.query(col[x] - 1) + splay.query(在 x 之前的节点个数)。
当然也可以写成:
1
2
3
4
5
| inline int query(int x)
{
splay(x);
return tr.query(col[x]) - siz[s[x][0]];
}
|
最后考虑修改。
我们发现修改就是 make_root,当然因为make_root 里已经有 access 了。
至于轻重链切换的时候,只要在树状数组里把原有的 splay 删掉,新增的 splay 加上就可以了,具体可以见代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| inline void access(int x)
{
for(int y = 0; x; x = fa[y = x])
{
splay(x);
s[x][1] = 0;
push_up(x);
tr.add(col[x], -siz[x]);
tr.add(nowcol, siz[x]);
s[x][1] = y;
push_up(x);
}
}
inline void make_root(int x)
{
nowcol++;
access(x);
splay(x);
fan(x);
col[x] = nowcol;
}
|
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
| #include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 200005;
const int maxq = 200005;
int n, q;
struct Edge
{
int to, nxt;
} e[maxn << 1];
int first[maxn];
inline void add_edge(int from, int to)
{
static int cnt = 0;
e[++cnt].nxt = first[from];
e[cnt].to = to;
first[from] = cnt;
e[++cnt].nxt = first[to];
e[cnt].to = from;
first[to] = cnt;
}
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
struct BIT
{
int xx[maxn << 1];
inline void add(int pla, int x)
{
for(; pla <= n + q; pla += lowbit(pla))
xx[pla] += x;
}
inline int query(int pla)
{
int ans = 0;
for(; pla; pla -= lowbit(pla))
ans += xx[pla];
return ans;
}
} tr;
int fa[maxn];
int s[maxn][2];
int siz[maxn];
int col[maxn];
int lzy[maxn];
inline void dfs(int now)
{
col[now] = now;
siz[now] = 1;
for(int i = first[now]; i; i = e[i].nxt)
{
register int to = e[i].to;
if(to != fa[now])
{
fa[to] = now;
dfs(to);
if(col[to] > col[now])
{
col[now] = col[to];
s[now][1] = to;
siz[now] = siz[to] + 1;
}
}
}
tr.add(col[now], 1);
}
inline bool nroot(int x)
{
return s[fa[x]][0] == x || s[fa[x]][1] == x;
}
inline void push_up(int x)
{
siz[x] = siz[s[x][0]] + siz[s[x][1]] + 1;
}
inline void fan(int x)
{
lzy[x] ^= 1;
swap(s[x][0], s[x][1]);
}
inline void push_down(int x)
{
if(lzy[x])
{
lzy[x] = 0;
if(s[x][0])
fan(s[x][0]);
if(s[x][1])
fan(s[x][1]);
}
if(s[x][0])
col[s[x][0]] = col[x];
if(s[x][1])
col[s[x][1]] = col[x];
}
inline void rotate(int x)
{
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y];
int d = s[y][1] == x, k = s[x][!d];
if(nroot(y))
s[z][s[z][1] == y] = x;
fa[x] = z;
s[x][!d] = y;
fa[y] = x;
s[y][d] = k;
if(k)
fa[k] = y;
push_up(y);
push_up(x);
}
int sta[maxn];
inline void splay(int x)
{
int tx = x;
int top = 0;
sta[++top] = tx;
while(nroot(tx))
sta[++top] = (tx = fa[tx]);
while(top)
push_down(sta[top--]);
while(nroot(x))
{
register int y = fa[x];
if(nroot(y))
{
register int z = fa[y];
rotate(((s[z][1] == y) ^ (s[y][1] == x)) ? x : y);
}
rotate(x);
}
}
int nowcol;
inline void access(int x)
{
for(int y = 0; x; x = fa[y = x])
{
splay(x);
s[x][1] = 0;
push_up(x);
tr.add(col[x], -siz[x]);
tr.add(nowcol, siz[x]);
s[x][1] = y;
push_up(x);
}
}
inline void make_root(int x)
{
nowcol++;
access(x);
splay(x);
fan(x);
col[x] = nowcol;
}
char opt[23];
inline int query(int x)
{
splay(x);
return tr.query(col[x]) - siz[s[x][0]];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &q);
nowcol = n;
for(int i = 1, f, t; i < n; ++i)
{
scanf("%d%d", &f, &t);
add_edge(f, t);
}
dfs(n);
int _u, _v;
for(int i = 1; i <= q; ++i)
{
scanf("%s", opt);
if(opt[0] == 'u')
{
scanf("%d", &_v);
make_root(_v);
}
else if(opt[0] == 'w')
{
scanf("%d", &_v);
printf("%d\n", query(_v));
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d", &_u, &_v);
int ans1 = query(_u);
int ans2 = query(_v);
printf("%d\n", ans1 < ans2 ? _u : _v);
}
}
return 0;
}
|



