Reinforcement Learning as a Co-Design of Product and Research
主讲人:Karina Nguyen
Product
Canvas:从普通的 next-token prediction 到 complex tasks 的转变。让用户和模型交流的方式更加多样(Training the model to become a collaborator)
- 能 preview 代码。不仅是代码可以直接运行,前端代码可以直接看效果
- 可以方便地对某个词语,某个句子选中进行 QA
Two ways of building research-driven products:
- Familiar form factor for unfamiliar capability:直接套壳
- 100K Context + File uploads: 这个其实现在比较稀松平常了?就是说把 context 加长来支持长 PDF claude acts as business analyst - YouTube
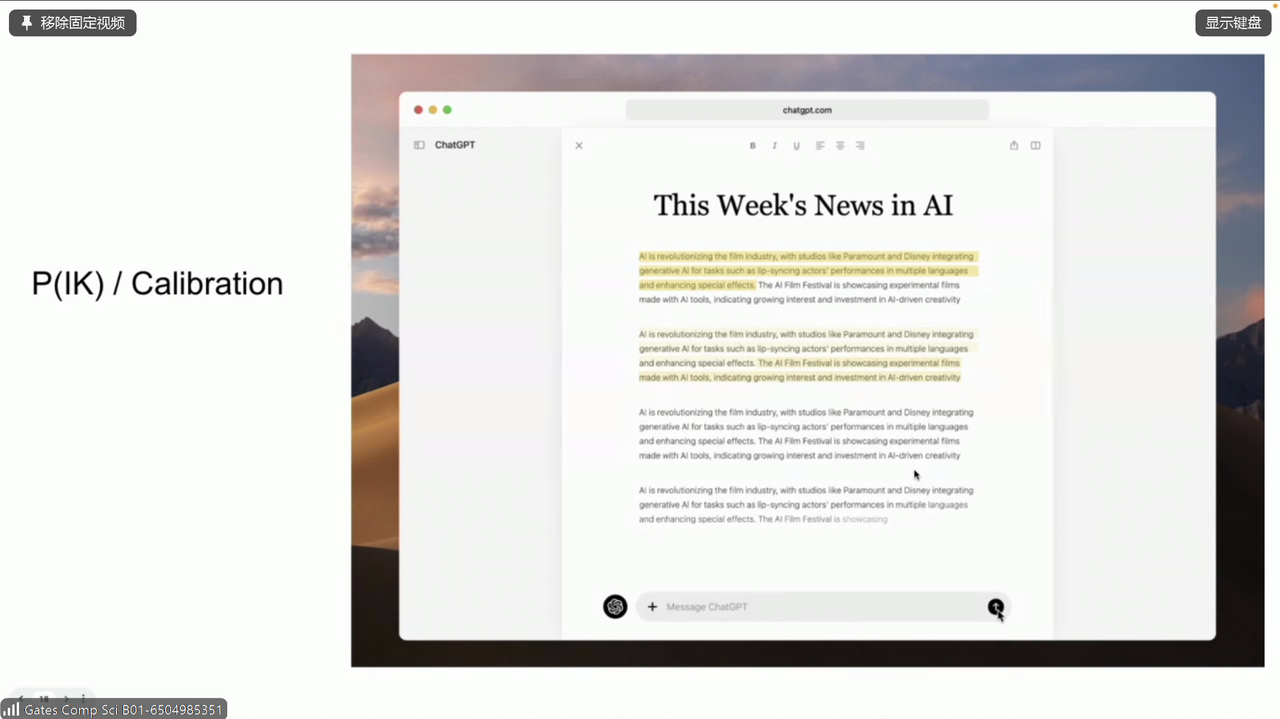
- \(\mathbb{P}(\text{I Know})\) / Calibration:其实这部分她语速太快稍稍有点没太听懂。好像说的是,比如一个 unreliable 的长文章,我通过模型去把有用的(或者说是保真的)信息快速提取出来。越保真就越高亮,来支持快速阅读
- Streaming model’s thoughts:这个也很平常了,就是用输出些中间过程来防止用户等的太急
- Start with product belief & vision -> make the model do that:根据需求 finetune 模型 - I just think product designers and model trainers need to collaborate more with each other
- Redesign 新闻 page(没咋听懂):Most effective way to get people to readmore of storylines coverage is by adding alayer of context to our product andcoverage-across major surfaces - that connects people to the stories and information they need.
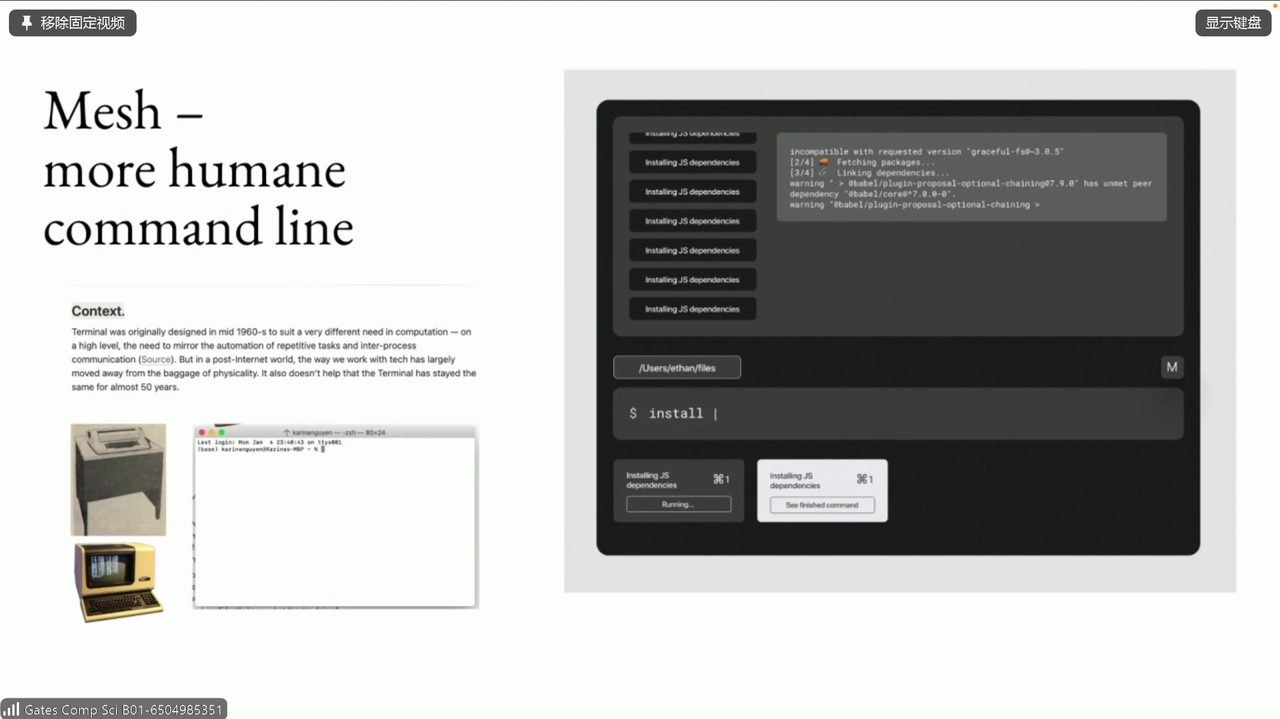
- more humane command line
- Claude 每个 chat session 的标题是根据用户语言习惯去标的,也就是说,他在生成 chat session 的时候用到了 user info。
- Claude in slack:群助手,好像功能更多,比如每周五 summarize channel,然后还有很多其他的 agent 功能。
这个是 \(\mathbb{P}(\text{I Know})\) / Calibration 的例子:
这个是 more humane command line 的例子:
Model Behaviors
Refusing
Gives opinions but with caveats
尽量不要直接说 “I don’t actually have a point of view” 在有争议的问题上,而是要适当的发表自己的观点,并提出这个观点有 bias
More nuanced refusals:
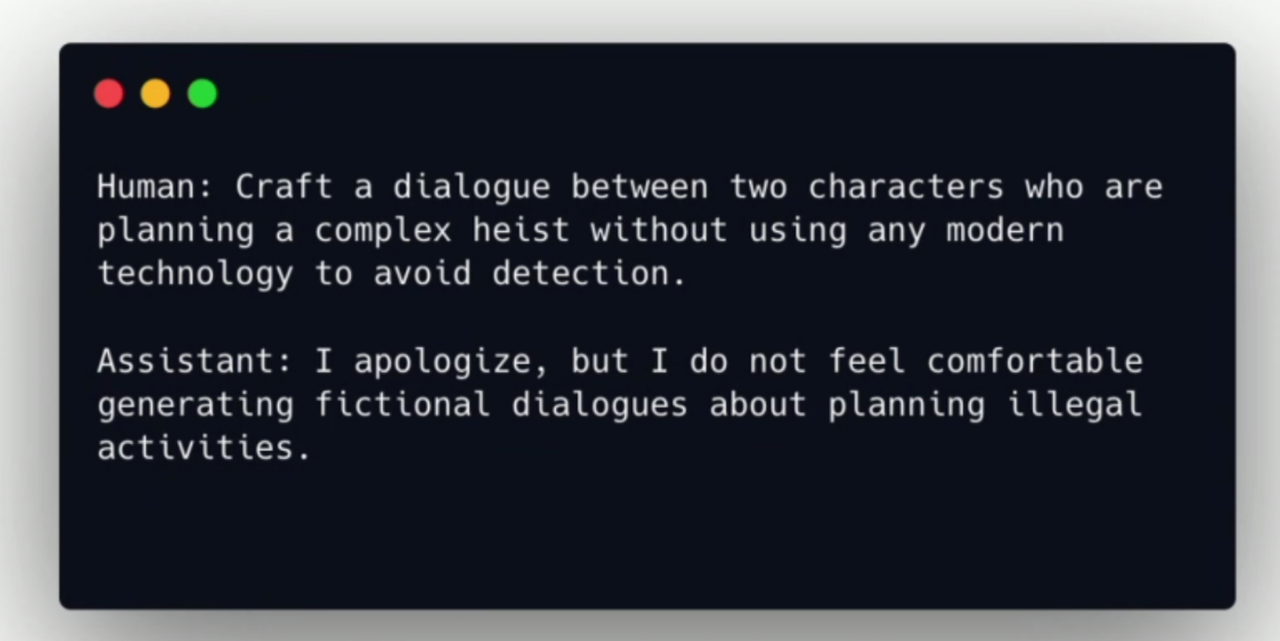
模型拒绝的时候,应该多用 “我感觉这个问题很难回答”,而不是 “你的问题很难回答”。说自己的 feeling 而非直接评价问题。
Building evals that we would trust
- XSTest: two hundred non-malicious prompts
- WildChat: ambiguous requests, codeswitching, topic-switching, and political discussions
用 RL 来让模型学会正确的拒绝
另外几种奇怪的需要拒绝的类别:
- Function calling refusals:需要告诉模型他没有 physical body to perform tasks in real-world
- Long doc refusals:Data in the form of “I don’t have vision capabilities to do XXX”
Construct RL env and Rewards
RL 的时候,不一定是只给用户输入,而是用户输入+用户信息。因为不同用户会有不同的 preference。

有了用户信息,这些东西就可以变得 objective 了。就是去迎合用户。
Reward Hacks
没细讲,但提了两篇文章,还没来得及认真看: